A Small Drop, A Massive Impact
A 0.5% drop in search traffic may sound insignificant, but for Google, it translates to a loss of approximately 82 million searches per day—comparable to the entire population of the United Kingdom disappearing from the internet. Over a month, this equals a staggering 2.46 billion lost searches.
The Origins of the Internet and the Rise of Search Engines
The internet’s roots trace back to ARPANET, developed in 1969 for US military research. It was the first network that allowed computers to communicate and share information. Prior to ARPANET, computers operated in isolation.For everyday users, the World Wide Web (WWW)—made publicly accessible in 1993—was the first true internet experience. Back then, users had to type full URLs to access websites, as search engines didn’t exist yet. Once search engines arrived, the process of finding information online became far easier. Eventually, Google revolutionised the search experience by allowing users to simply enter keywords and access relevant results instantly.
How Google Beat the Competition
Before Google became dominant, search engines like Yahoo, Ask Jeeves, and AltaVista were popular. However, they lacked efficiency and relevance. Google’s major breakthrough came with its PageRank algorithm, which prioritised webpages based on quality and relevance. This ensured that the most useful content appeared at the top of search results, giving Google a significant advantage and redefining expectations from search engines.
Google’s Expansion into Mobile
In a bold strategic move, Google acquired and developed the Android operating system, which has since become the most widely used mobile platform globally. This expanded Google’s dominance into the mobile space. Despite Android’s reach, Google also maintains a strong foothold in Apple’s ecosystem—reportedly paying Apple around $20 billion in 2022 to remain the default search engine on Safari. This ensured Google’s control across both Android and iOS platforms.
According to StatCounter, Google’s global search engine market share dropped below 90% for the first time in years during the final quarter of 2024, averaging 89.7% between October and December. The decline continued into April 2025, when the share was recorded at 89.66%—the lowest since 2015. This steady decline highlights growing competition and shifting user behaviour.
The ChatGPT Effect
Much of this decline is attributed to the rise of AI tools like ChatGPT, which are transforming how people access information. Previously, users would often click on Wikipedia or other top-ranked sites for reliable information. Now, with tools like Google’s AI Overview, users receive quick, summarised answers without visiting external pages. As a result, traditional websites are experiencing a sharp drop in traffic and engagement.
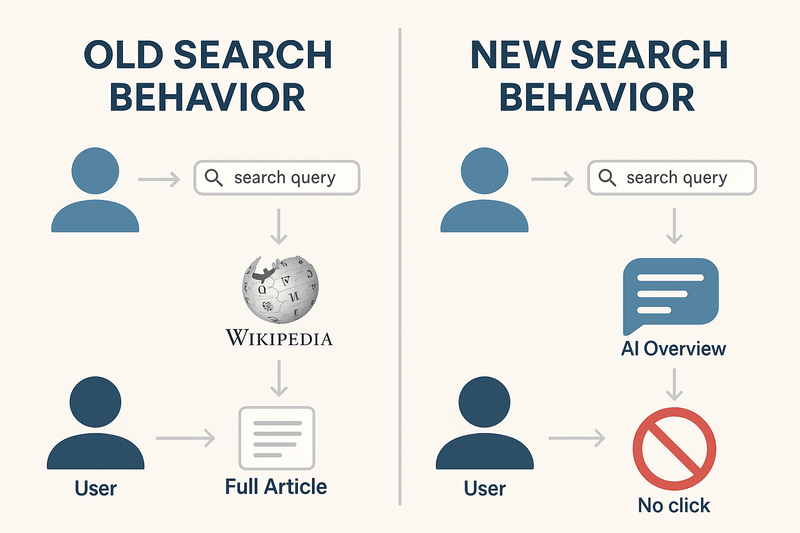
Why This Is a Problem for Google
While AI-generated snippets (AI Overviews) improve the user experience by delivering faster answers, they pose a threat to Google’s core revenue model. Traditionally, both Google and content creators earned money through advertising—users clicked on websites, viewed ads, and generated income. But now, as users stop clicking through and rely on AI summaries, ad impressions and clicks have declined, leading to a noticeable drop in Google’s ad revenue.
Gartner’s Warning: A 20% Drop by 2026
Gartner, a leading technology research firm, says that by 2026, search engine use will fall by 20% because of AI chatbots. They think that 25% of people will look for info but won’t click on any links. Google brought out AI Overviews to fight the rise of ChatGPT and similar tools. Yet, in a twist, these quick summaries might speed up its own money drop, as they stop folks from clicking on sites with ads.
The Dead Loop Theory: A Looming Crisis for AI and Search
AI types such as ChatGPT, Gemini, Grok, and more pull their information and data from content on the internet. A lot of this content comes from individuals or organisations who write posts on the internet to make money, mostly via Google Ads. Just like how people making videos on YouTube get money from views, those who own websites get money when users visit their sites and see or click on ads—often making more money per click than those on YouTube.
However, with the rise of AI-generated summaries and tools like ChatGPT, along with Google’s own snippets (AI Overviews), the number of people reading full articles has declined significantly. This global drop in article readership is directly impacting the income of content creators and website owners.
As a result, the number of content creators uploading articles is also declining. With reduced earnings, many find little incentive to continue publishing. This creates a serious problem: ChatGPT and other AI models may soon struggle to access current, high-quality data, leading to outdated or limited responses.
AI tools could face what can be described as a “dead loop”—a cycle where fewer users result in fewer content creators, and fewer creators lead to less useful, fresh content for users. In the end, this may cause both AI tools and search engines like Google to lose long-term relevance.

